São Tomé
| São Tomé |
|
São Tomé palace |

Flag |

Coat of arms |
|
|
Location on São Tomé Island
|
| Coordinates: |
| Country |
 São Tomé and Príncipe São Tomé and Príncipe |
| Province |
São Tomé Island |
| District |
Água Grande |
| Time zone |
UTC (UTC+0) |
| Area code(s) |
+239-11x-xxxx through 14x-xxxx |
São Tomé (population 56,166 in 2005) is the capital city of São Tomé and Príncipe and is by far that nation's largest town. Its name is Portuguese for "Saint Thomas".
History
São Tomé was founded by Portugal in 1485. The Portuguese came to São Tomé in search of land to grow sugar. The island was uninhabited before the arrival of the Portuguese sometime around 1470. São Tomé was right on the equator and wet enough to grow sugar in wild abundance. Its proximity to the African Kingdom of Kongo provided an eventual source of slave laborers to work the sugar plantations. São Tomé is centred on a sixteenth century cathedral. Another early building is Fort São Sebastião, built in 1575 and now the São Tomé National Museum. In 1599, the city as well as the islands were taken by the Dutch for two days and again in 1641 for a year. It was the then colony's capital until 1753 and has been the national capital continuously since 1852.
Geography and location

The cathedral - Sé - of Sao Tomé
São Tomé is located at . [1]
Important as a port, São Tomé is located on Ana Chaves Bay in the northeast of São Tomé Island, and Ilhéu das Cabras lies nearby offshore. São Tomé is located northeast of Trindade, southeast of Guadalupe and northwest of Santana. It is linked to these towns by various roadways, but especially by the highway encircling the entire island of São Tomé.
Features of the town include the Presidential Palace, the Fisherman's Church, and a cinema. The city is also home to schools, middle schools, high schools, two markets, a radio station, a television station RFI, a hospital, São Tomé International Airport, and many squares (praças). São Tomé also serves as the center of the island's road and bus networks. The town is well known for the Tchiloli play.
Population history

São Tomé market
| Year |
Population |
Change |
Density |
| 1990 (June 23, Census) |
42,331 |
- |
- |
| 2000 (June 16, Census) |
49,997 |
- |
- |
| 2003 (Computing) |
53,300 |
- |
- |
| 2005 (January 1, Computing) |
56,166 |
- |
- |
Economy
São Tomé is served by São Tomé International Airport (IATA: TMS, ICAO: FPST) with regular flights to Europe and other African Countries.
Climate
São Tomé features a tropical wet and dry climate with a relatively lengthy wet season and a short dry season. The wet season runs from October through May while the dry season covers the remaining four months. São Tomé sees on average just under 1000 mm of precipitation per year. Temperatures in the city are relatively constant, with average high temperatures usually around 30°C and average low temperatures around 22°C.
| Climate data for São Tomé |
| Month |
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
Jun |
Jul |
Aug |
Sep |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
Year |
| Source: BBC Weather [1] |
References
External links
| Capitals of São Tomé and Príncipe |
 |
| Provincial Capitals of São Tomé and Príncipe: Santo António · São Tomé |
| District Capitals of São Tomé and Príncipe: Guadalupe · Neves · Santana · Santo António · São João dos Angolares · São Tomé · Trindade |
|
Portuguese Empire |
|
North Africa
|
15th century
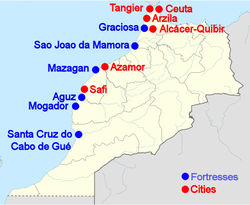
1415–1640 Ceuta
1458–1550 Alcácer Ceguer (El Qsar es Seghir)
1471–1550 Arzila (Asilah)
1471–1662 Tangier
1485–1550 Mazagan (El Jadida)
1487– middle 16th century Ouadane
1488–1541 Safim (Safi)
1489 Graciosa
|
16th century
1505–1769 Santa Cruz do Cabo de Gué (Agadir)
1506–1525 Mogador (Essaouira)
1506–1525 Aguz (Souira Guedima)
1506–1769 Mazagan (El Jadida)
1513–1541 Azamor (Azemmour)
1515 Sao Joao da Mamora (Mehdya)
1577–1589 Arzila (Asilah)
|
|
Southwest Asia
|
16th century
1506–1615 Gamru (Bandar-Abbas)
1507–1643 Sohar
1515–1622 Hormuz (Ormus)
1515–1648 Quriyat
1515–? Qalhat
1515–1650 Muscat
1515?–? Barka
1515–1633? Julfar (Ras al-Khaimah)
1521–1602 Bahrain (Muharraq and Manama)
1521–1529? Qatif
1521?–1551? Tarut Island
1550–1551 Qatif
1588–1648 Matrah
|
17th century
1620–? Khor Fakkan
1621?–? As Sib
1621–1622 Qeshm
1623–? Khasab
1623–? Libedia
1624–? Kalba
1624–? Madha
1624–1648 Dibba Al-Hisn
1624?–? Bandar-e Kong
|
|
East Asia and Oceania
|
16th century
1511–1641 Portuguese Malacca
1512–1621 Moluccas (Maluku Islands)
1522–1575 Ternate
1576–1605 Ambon
1578–1650 Tidore
1512–1665 Makassar
1553–1999 Macau
1533–1545 Ningbo
1571–1639 Decima (Dejima, Nagasaki)
|
17th century
1642–1975 Portuguese Timor (East Timor)1
19th century
Macau
1864–1999 Coloane
1849–1999 Portas do Cerco
1851–1999 Taipa
1890–1999 Ilha Verde
20th century
Macau
1938–1941 Lapa and Montanha (Hengqin)
|
|
1 1975 is the date of East Timor's Declaration of Independence and subsequent invasion by Indonesia. In 2002, the independence of East Timor was recognized by Portugal and the rest of the world.
|
North America and the North Atlantic Ocean
Central and South America
|
16th century
1500–1822 Brazil
1536–1620 Barbados
|
17th century
1680–1777 Nova Colônia do Sacramento
19th century
1808–1822 Cisplatina (Uruguay)
|
Portuguese colonization of the Americas
Theory of Portuguese discovery of Australia
|
|
|
Capitals of Africa |
|
| |
Abuja, Nigeria
Accra, Ghana
Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Algiers, Algeria
Antananarivo, Madagascar
Asmara, Eritrea
Bamako, Mali
Bangui, Central African Republic
Banjul, Gambia
Bissau, Guinea-Bissau
Bloemfontein, South Africa1
Brazzaville, Rep. Congo
Bujumbura, Burundi
Cairo, Egypt
Cape Town, South Africa2
|
Conakry, Guinea
Dakar, Senegal
Djibouti, Djibouti
Dodoma, Tanzania
Freetown, Sierra Leone
Gaborone, Botswana
Harare, Zimbabwe
Hargeisa, Somaliland4
Jamestown, Saint Helena
Kampala, Uganda
Khartoum, Sudan
Kigali, Rwanda
Kinshasa, DR Congo
Libreville, Gabon
Lilongwe, Malawi
|
Lobamba, Swaziland2
Lomé, Togo
Luanda, Angola
Lusaka, Zambia
Malabo, Equatorial Guinea
Mamoudzou, Mayotte
Maputo, Mozambique
Maseru, Lesotho
Mbabane, Swaziland3
Mogadishu, Somalia
Monrovia, Liberia
Moroni, Comoros
Nairobi, Kenya
N'Djamena, Chad
Niamey, Niger
|
Nouakchott, Mauritania
Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
Port Louis, Mauritius
Porto-Novo, Benin
Praia, Cape Verde
Pretoria, South Africa3
Rabat, Morocco
Saint-Denis, Réunion
São Tomé, São Tomé and Príncipe
Tripoli, Libya
Tunis, Tunisia
Victoria, Seychelles
Windhoek, Namibia
Yaoundé, Cameroon
Yamoussoukro, Côte d'Ivoire
|
|
|
| 1 Judicial. 2 Parliamentary. 3 Executive. 4 an unrecognized or partially recognized state |
|